Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Compiled & Edited by: Dr. Sobin C.B, MD DNB
Consultant Gastroenterologist
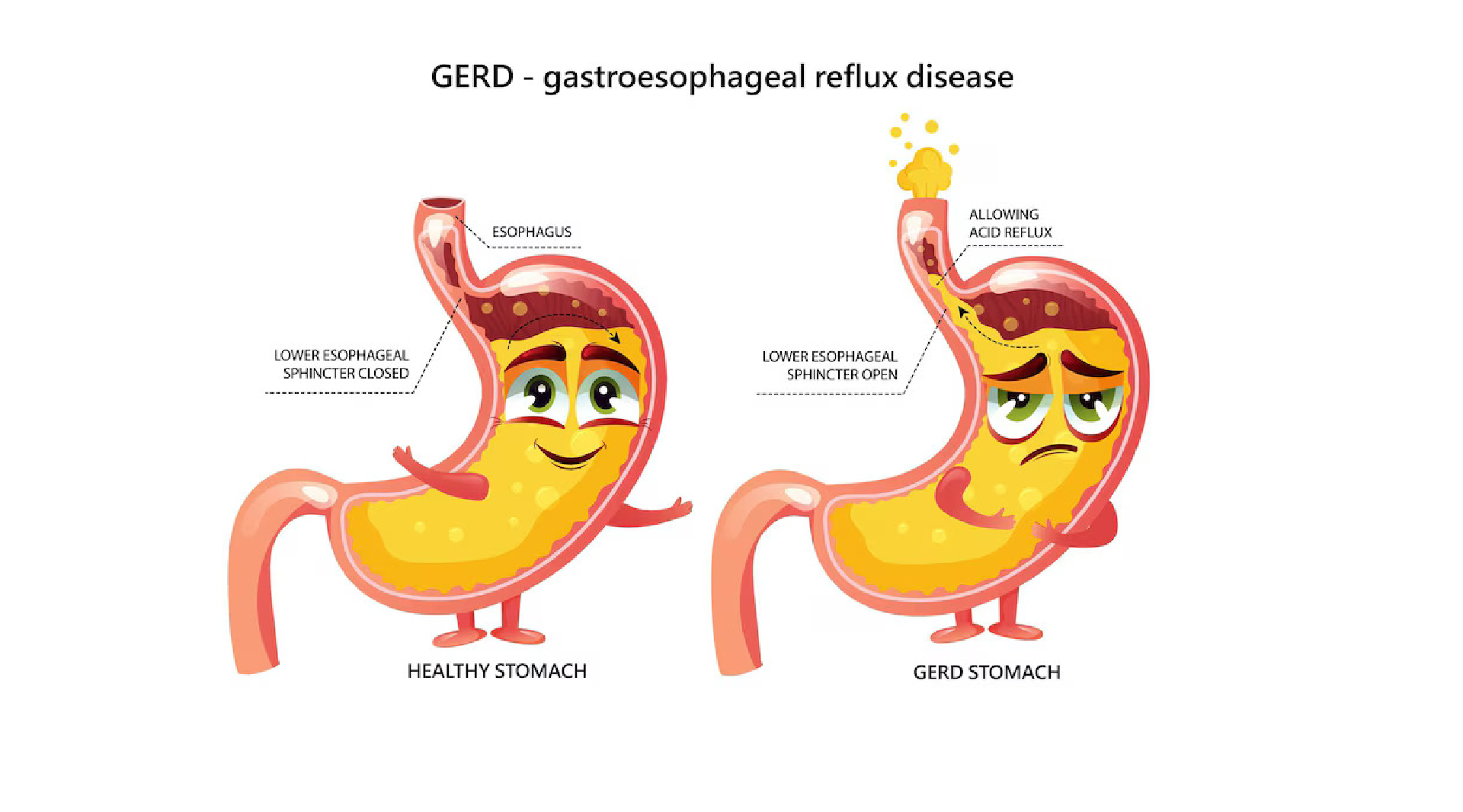
Heartburn, also known as Acid reflux, or Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a chronic digestive illness. It occurs when stomach acid refluxes back into the food pipe. As a result, the lining of the oesophagus becomes irritated and damaged.
GERD is a condition that has no single cause; rather, it develops as the muscle valve that closes off the stomach from the oesophagus weakens, enabling stomach acid to flow back into the oesophagus.
Symptoms of GERD:
○ Burning sensation of the chest, spreading from the stomach to the throat.
○ Burping
○ Bloated stomach
○ Bitter taste in the mouth
○ Chest pain
○ Cough
○ Discomfort in the chest
○ Difficulty swallowing
○ Feeling of a lump in the throat
○ Hoarseness of voice
○ Constant sore throat
Risk factors for GERD:
○ Foods - fried, spicy, or fatty foods, chocolate, coffee, carbonated beverages
○ Some medications for asthma, antihistamines, antidepressants calcium blockers, painkillers and sedatives
○ Obesity or pregnancy-induced high abdominal pressure
○ Hormonal changes
○ Alcohol
○ Smoking
○ Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
○ Scleroderma
Potential complications of GERD:
○ Reflux laryngitis
○ Oesophageal strictures or ulcers,
○ Barrett’s oesophagus,
○ Increases the risk of oesophageal cancer
○ Chronic cough
Diagnosis of GERD:
If acid reflux occurs more than twice a week for separate weeks, it could be a sign of GERD. If your symptoms worsen, or you experience nausea, vomiting or difficulty swallowing, consult your doctor. Based on symptoms and medical history, your doctor may suggest interventions to manage your condition.
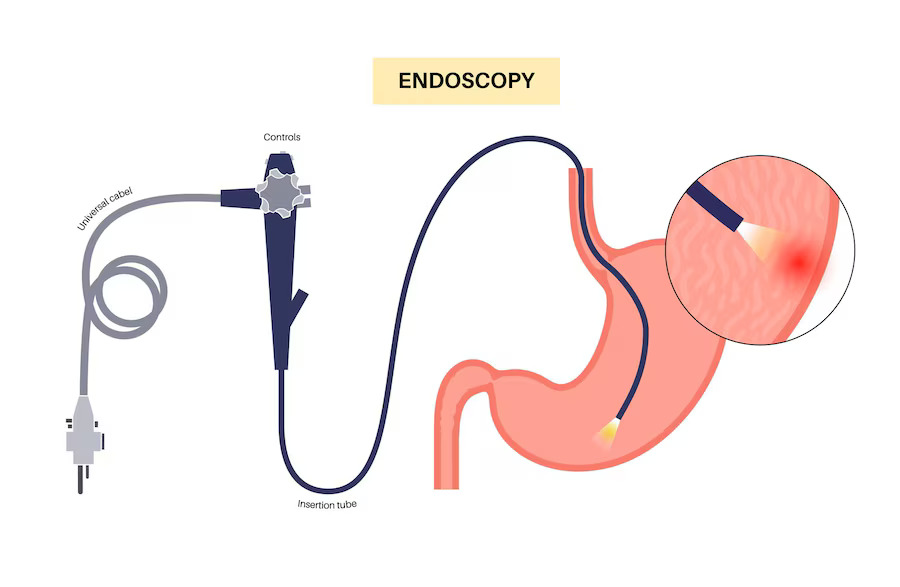
Your doctor may recommend the following tests:
○ Endoscopy to examine the lining of upper gastrointestinal tract.
○ Test to measures the amount of acid in the oesophagus.
○ Oesophageal manometry to check the strength of the sphincter muscles.
Treatment of GERD:
Depending on the severity of the condition, your doctor will evaluate and suggest the most suitable treatment. Treatment options include:
1. Lifestyle and dietary changes
○ Avoiding late meals
○ Avoiding food that induces your acid reflux- fried, spicy, fatty foods, chocolate, coffee, or carbonated beverages
○ Maintaining a healthy weight
○ Eating smaller meals
○ Raising your pillow
○ Elevating the head-side of your bed 15 degrees
○ Avoiding eating two hours before sleeping.
○ Avoiding tight fitting clothing
○ Limiting alcohol consumption
○ Quitting smoking
2. Prescription medications:
○ To reduce acid production in the stomach
○ To help accelerate stomach emptying
○ Acid suppressors or antacids
○ Other medicines used to relieve other symptoms
3. Surgery
○ Surgery is recommended only if your GERD symptoms fail to improve with lifestyle changes and medicine.
○ Fundoplication surgery is done using a laparoscope to increase pressure at the lower end of the oesophagus and reduce reflux. It often leads to long-term reflux control.
○ Another, newer treatment modality is using of RF waves through endoscope to tighten the sphincter muscle.
Talk to our gastroenterologist to know more.